By Thoma Friedman, The New York Times, September 7, 2016
Editor's note: In his today's New York Times column Thomas Freidman discusses the anthropogenic mass extinction after attending the International Union of Conservation Scientists in Hawaii. However, when it comes to explaining what drives the mass extinction he points a finger at "us." But humanity is not one homogeneous mass. 80% of world consumption occurs in the Global North with 20% of the world population. 80% of the population in the Global South conume only 20% of the world resources and more than 2.1 billion of them lived on less than US $ 3.10 a day in 2012. Clearly, we are not all equally responsible for the Great Sixth Extinction. But what is?
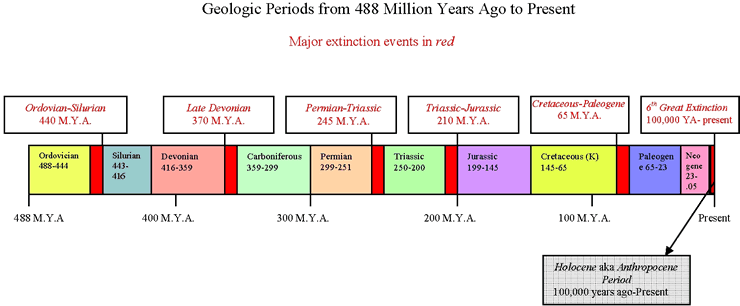
Friedman properly give prominence to E.O. Wilson's Half-Earth in which the prominent Harvard biologist proposes to set aside half the planet's land and ocean as protected wildlife reserve. But he fails to mention that E. O. Wilson concurs with other scientists that the Anthropocene (The Age of Man) is responsible for the sixth great mass extinction crisis. The Working Group on the Anthropocene, reported to the recently concluded International Geology Congress in South Africa at the end of August that the Holocene has ended and we are now living in the Age of Man (the Anthropocene) because of the Earth System changes the modern society has brought about. In fact, scientists have already noted nine planetary boundaries that have been or are being crossed due to the Great Acceleration that began approximately in 1950 with the rapid growth of the fossil-fuel powered world industrial capitalist economy. The two core boundaries are climate change and biodiversity loss. The omission of the Anthropocene in Friedman's discussion is a great disservice to the public because by understanding it and its immediate causes it becomes clear that manifestations of the planetary crisis are rooted in the socioeconomic system we live in and therefore the need to organzie a public discussion of how to moved beyon it order to stop and reverse the crisis. KN
Friedman properly give prominence to E.O. Wilson's Half-Earth in which the prominent Harvard biologist proposes to set aside half the planet's land and ocean as protected wildlife reserve. But he fails to mention that E. O. Wilson concurs with other scientists that the Anthropocene (The Age of Man) is responsible for the sixth great mass extinction crisis. The Working Group on the Anthropocene, reported to the recently concluded International Geology Congress in South Africa at the end of August that the Holocene has ended and we are now living in the Age of Man (the Anthropocene) because of the Earth System changes the modern society has brought about. In fact, scientists have already noted nine planetary boundaries that have been or are being crossed due to the Great Acceleration that began approximately in 1950 with the rapid growth of the fossil-fuel powered world industrial capitalist economy. The two core boundaries are climate change and biodiversity loss. The omission of the Anthropocene in Friedman's discussion is a great disservice to the public because by understanding it and its immediate causes it becomes clear that manifestations of the planetary crisis are rooted in the socioeconomic system we live in and therefore the need to organzie a public discussion of how to moved beyon it order to stop and reverse the crisis. KN
* * *
HONOLULU — Robert Macfarlane, in his book “Landmarks,” about the connection between words and landscapes, tells a revealing but stunning story about how recent editions of the Oxford Junior Dictionary (aimed at 7-year-olds) dropped certain “nature words” that its editors deemed less relevant to the lives of modern children. These included “acorn,” “dandelion,” “fern,” “nectar,” “otter,” “pasture” and “willow.” The terms introduced in their place, he noted, included “broadband,” “blog,” “cut-and-paste,” “MP3 player” and “voice-mail.”
While this news was first disclosed in 2015, reading it in Macfarlane’s book still shocks me for what it signifies. But who can blame the Oxford editors for dumping Amazon words for Amazon.com ones? Our natural world is rapidly disappearing. Just how fast was the major topic here last week at the global conference held every four years by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, which I participated in along with some 8,000 scientists, nature reserve specialists and environmentalists.
The dominant theme running through the I.U.C.N.’s seminars was the fact that we are bumping up against and piercing planetary boundaries — on forests, oceans, ice melt, species extinctions and temperature — from which Mother Nature will not be able to recover. When the coral and elephants are all gone, no 3-D printer will be able to recreate them.
In short, we and our kids are rapidly becoming the Noah generation, charged with saving the last pairs. (This is no time to be electing a climate-change denier like Donald Trump for president.)
Sylvia Earle, the renowned oceanographer, put it well to a sustainability conference hosted here by the East-West Center alongside the I.U.C.N. meetings. In her lifetime, said Earle, she has felt as if she’s been “witness to the greatest era of discovery and the greatest era of loss” in our planet’s history.
So now, she said, “we are at a crossroads. What we do right now or fail to do will determine the future — not just for us, but for all life on earth.”
Those really are the stakes — there is a reason nature words are being removed from children’s dictionaries. Last week, for instance, The Times reported on a study that revealed how “the African elephant population is in drastic decline, having shrunk about 30 percent from 2007 to 2014. … The deterioration is accelerating: Largely because of poaching, the population is dropping 8 percent a year, according to the Great Elephant Census. … Patricia Awori, an official with the African Elephant Coalition, said, ‘These numbers are shocking.’”
O.K., so you don’t care that your kids may never see an elephant in the wild, only in a zoo. That’s not all. The species extinction rate is now about “1,000 times faster than before the global spread of humanity,” explained the great biodiversity expert E. O. Wilson, another speaker here. “Half of the species described today will be gone by the end of the century, unless we take drastic action.”
These species, he noted, evolved over 3.5 billion years “to create an exquisite and careful balance of interconnected resilience.” These plants and animals and their ecosystems sustain the foundations of life on which we depend. When we lose the trees that maintain watersheds, the coastal mangroves that protect against storm surges, the glaciers that store fresh water and the coral reefs that feed fish, we humans become less resilient. Indeed, strip them all away, said Wilson, “and the world as we know it will unravel.”
The magazine Discover just noted that we’ve been tracking average temperature over global land and ocean surfaces since 1880 — or for 1,639 months. Due to global warming, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration reported that July 2016 was the hottest “of all 1,639 months on record.”
That is why the actress Alison Sudol, an I.U.C.N. good-will ambassador, opened the plenary by observing that our planet is now “under attack” — by us.
“Our vast oceans, full of mysteries and wonders, are thick with plastic and mercury,” she noted. “Rain forests — abundant sources of oxygen and medicine; land of ancient lore and tradition; home to thousands of species of wildlife, many as yet unknown to us — are being plowed down before we have a chance to properly discover what it is we are losing.
“These are lungs of the earth, the oceans and the forests, and we are destroying them. Deeply, desperately, we are hoping someone will do something before it is too late. That someone we are hoping for is you.”
So do we have a plan? Wilson has one — a big, audacious plan. It’s the title of his latest book, “Half-Earth,” a call to action to commit half of the planet’s surface — land and oceans — to protected zones.
Right now, the I.U.C.N. says, close to 15 percent of the earth’s land and 10 percent of its territorial waters are covered by national parks and protected areas. If we protect half the global surface, Wilson argues, the fraction of species protected will be about 85 percent, which would keep life on earth, including the human species, in a safe zone.
No comments:
Post a Comment